3PE anti-corrosion pipe is a kind of pipe product that strengthens the protection of steel pipe through three-layer composite coating technology. Its anti-corrosion layer is composed of FBE bottom layer, adhesive middle layer and high density polyethylene (HDPE) outer layer, forming a collaborative protection system with both chemical stability and physical resistance.
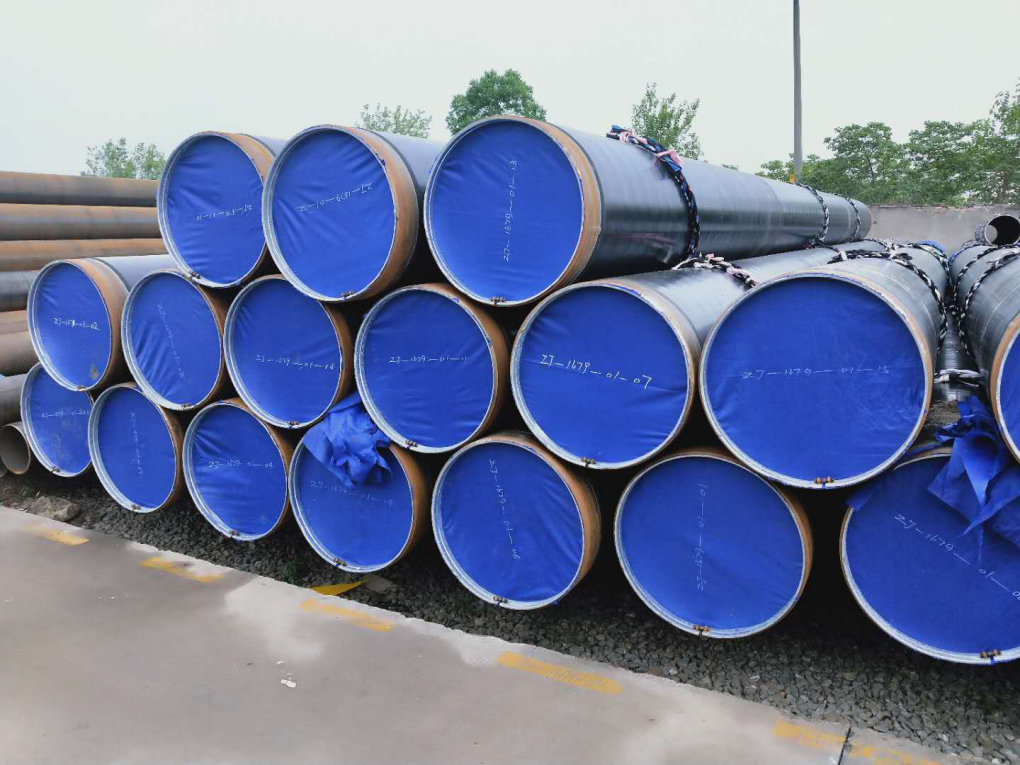

- 3LPE & 3LPP
3PE Anti-corrosion Steel Pipe Epoxy Coating Reinforce Grade Gas Pipeline
Email:
sales@imristeel.com
Phone:
+86 13646172523
Quote Now
Product Detail
Packaging & Delivery
Related Products
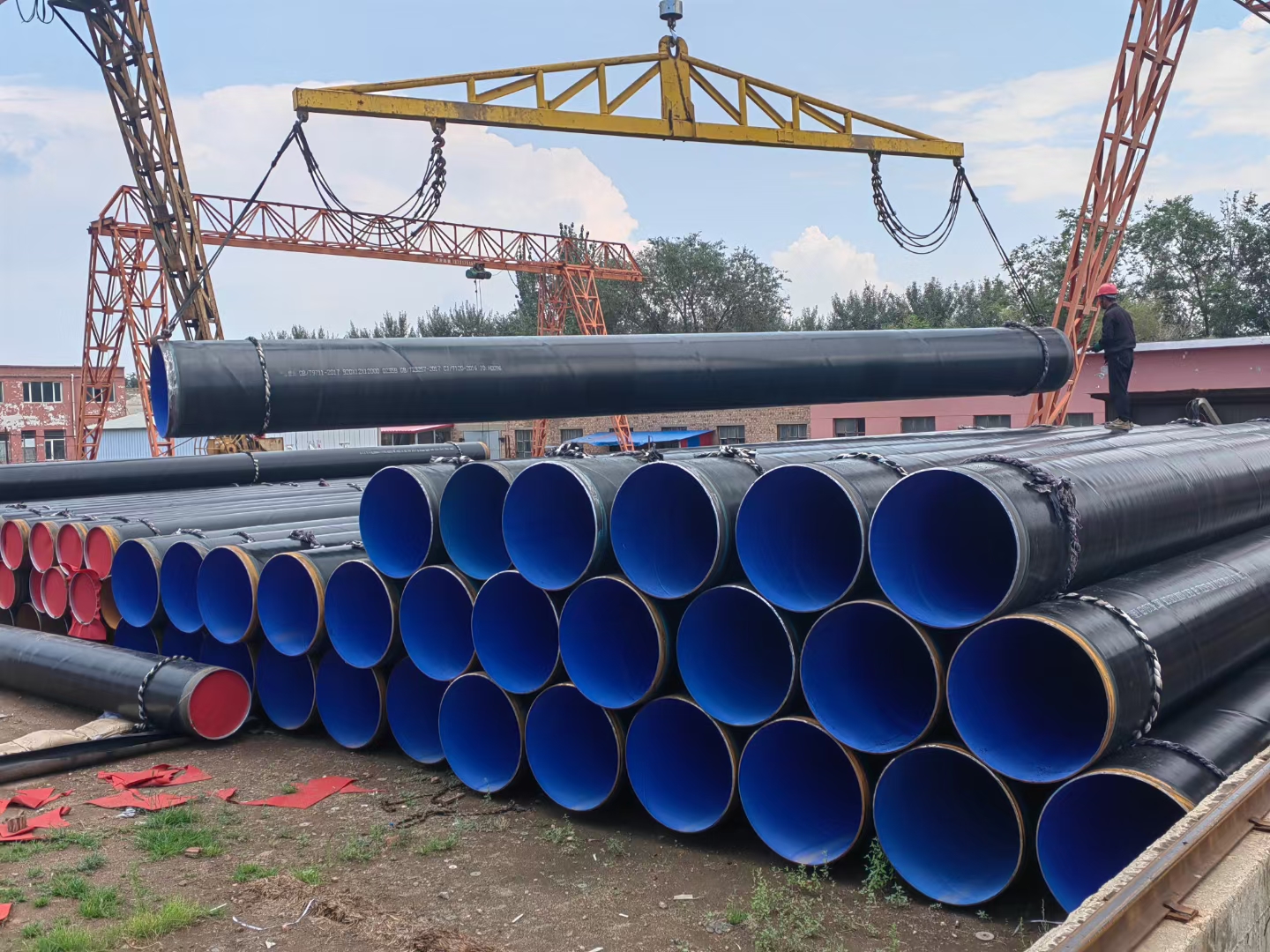
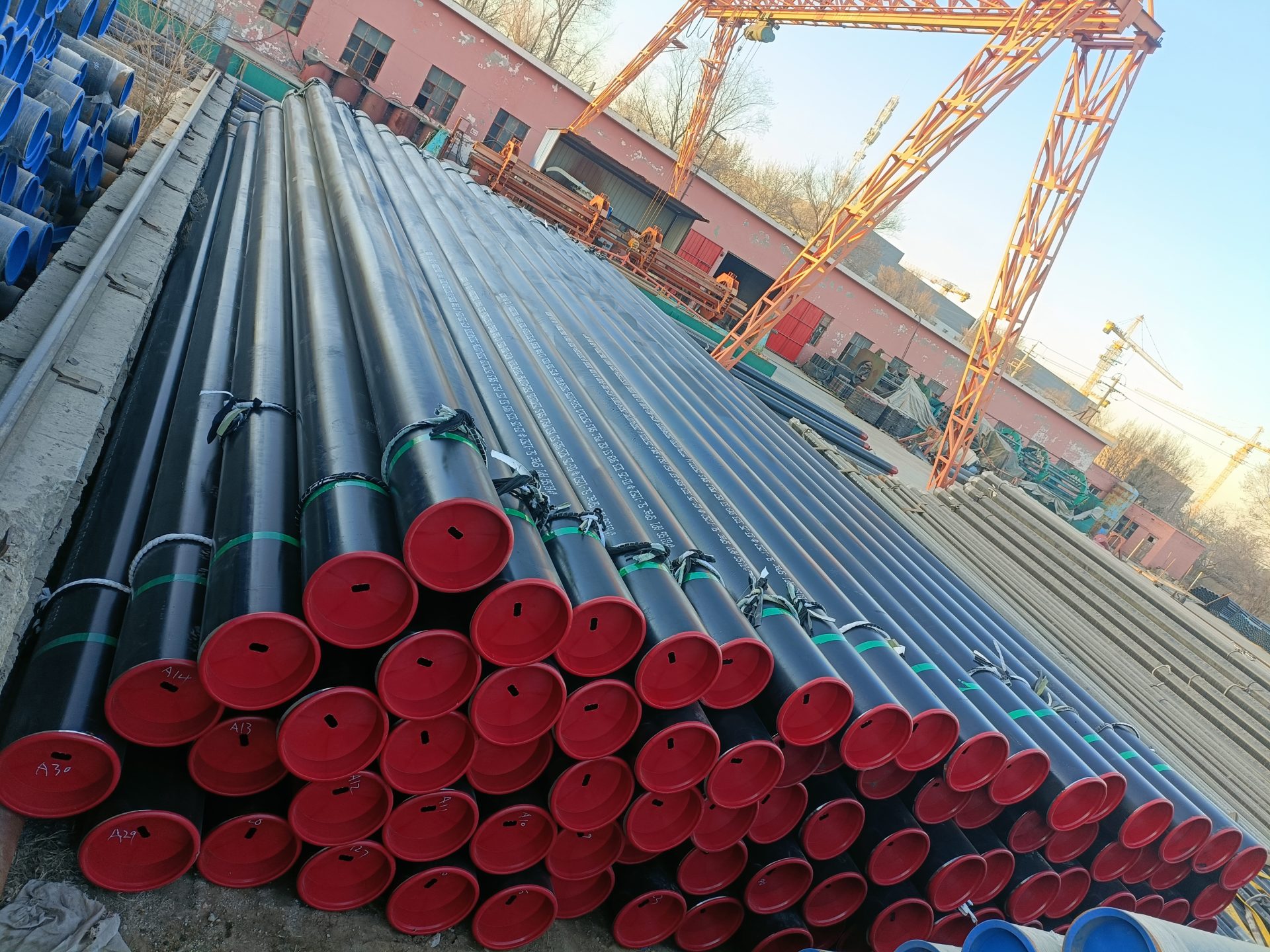


Product Detail
| Product Description | ||
| Product Name | 3PE Anti-corrosion Steel Pipe Epoxy Coating Reinforce Grade Gas Pipeline | |
| Standard | DIN30670,NF A49-710,CAN/CSAZ245.21,ISO DIS21809-1,GB/T23257,SY/T0413 | |
| Size | Outer Diameter | 32-1620mm |
| Wall Thickness | 2.9-60mm or customized | |
| Length | 5-12m or customized | |
| Surface Treatment | External:3PE | |
| Internal:Liquid Epoxy | ||
| Layer Tolerance | ±10% | |
| Features | Strong bonding strength,good insulation performance,mechanical shock resistance,long service life,and small cathodic protection current density,etc. | |
| Application | Suitable for the underground water supply and drainage in coal mines down hole shotcrete, ventilation of positive and negative pressure,waste residue of process water,backwater and long-distance underground pipelines for oil,water,and gas,etc. | |
| Min.Order | 25 tons,more quantity price will be lower | |
| End | Plain,beveled,cutting,threading.flange or customized | |
| End Protector | Plastic pipe caps,iron protector or customized | |
| Package | 1.Bundling with steel strip. 2.Oiled and packing with plastic wrap 3.In bulk. 4.Packing in woven bags. 5.As customer’s requirement | |
| Shipping | 1.Length 2.Length>/=6.0 Meters,Loaded in 40 Feet Container | |
| Delivery Time | Normally within 15 days and according to the quantity. | |
Manufacture Technique
1.Pretreatment of the steel pipe surface
The oxide skin, oil pollution and impurities on the surface of the steel pipe are removed by shot blasting and rust removal process to achieve the cleanliness of Sa 2.5 level (ISO 8501-1 standard), and the surface roughness of 50-90 μ m is formed to enhance the adhesion of the coating. Then use compressed air to dust to ensure that the substrate is clean and dry.
2.Coating
Preheat with the FBE bottom coating
The steel tube is heated to 180-220℃ by intermediate frequency induction, and the molten epoxy powder (FBE) is evenly covered on the surface by electrostatic spraying technology. At high temperature, FBE melts and solidifies to form a dense bottom layer of 80-150 μ m, which has excellent cathode peel resistance and chemical corrosion resistance, and strong adhesion of acid and alkali resistance.
Coating of adhesive in middle layer
When the FBE layer is still in a molten state, coat the vinyl-acrylic acid copolymer (EAA) or vinyl-vinyl acetate copolymer (EVA) adhesive with a thickness of approximately 170-250 μ m. The adhesive is chemically bonded with the FBE and the subsequent HDPE layer at high temperature to effectively prevent the interlayer peeling.
HDPE outer layer molding
After heating and melting the high density polyethylene (HDPE) particles, the extruder spiral is wound around the adhesive layer and coated by extrusion winding process to form a 1.8-3.7mm thick outer protective layer. The HDPE layer is quickly finalized by water cooling, and has strong mechanical impact resistance, ultraviolet resistance and waterproof permeability, and adapts to the complex geological and climate environment.
3.Cooling setting
Through the rapid cooling of the water cooling system, the HDPE layer is crystalline and solidified, forming a protective shell with mechanical damage resistance and strong weather resistance.
Quality inspection and repair
1.Electric spark detection: use 15-30kV high voltage detector to scan the coating and check the pinhole, crack and other defects.
2.Thickness test: Magnetic thickness tester verifies that the thickness of each layer meets the ISO 21809 or DIN 30670 standards.
3.Adhesion test: peel test is used to ensure that the bonding strength of the adhesive layer is greater than or equal to 70N/cm.
When defects are found, they should be partially polished and remelted to ensure the integrity of the protective layer.
Packaging & Delivery

Packaging & Delivery
· Packaging Details: Bundles wrapped with strong steel trips, caps on two ends of every pipe or according to customers’ requirements.
· Port: Tianjin Port
· Lead Time: Within 20-30 days depends on the order quantity
Packaging & Shipping
· Minimum order quantity: 5 tons
· Price: FOB or CIF or CFR at Xin’gang port in Tianjin
· Payment: 30% deposit in advance, the balance against the copy of B/L; or 100% L/C, etc
· Lead Time: within 10-25 workdays normally
· Packing: Standard seaworthy packing or as per your request .(as pictures)
· Sample: Free sample is available.
· Price: FOB or CIF or CFR at Xin’gang port in Tianjin
· Payment: 30% deposit in advance, the balance against the copy of B/L; or 100% L/C, etc
· Lead Time: within 10-25 workdays normally
· Packing: Standard seaworthy packing or as per your request .(as pictures)
· Sample: Free sample is available.
Related products


Seamless Pipe
Read More 




GB/T 8162 Seamless Carbon Steel round Pipe for Structure
Read More 




Seamless Pipe
Read More 




3PE Anti-corrosion Steel Pipe Epoxy Coating Reinforce Grade Gas Pipeline
Read More 




demo1
Read More 




Seamless Pipe
Read More 




3PE Anti-corrosion Steel Pipe Epoxy Coating Reinforce Grade Gas Pipeline1
Read More 



Outside diameter 406mm seamless pipeline pipe for oil gas field
Read More 







