Line pipe transports oil, gas, and water in energy infrastructure. Available in seamless and welded types, it features plain, threaded, or beveled ends for welding, coupling, or mechanical connections. Manufactured to API 5L, ISO 3183, and ASTM standards, it ensures high strength, corrosion resistance, and durability for demanding industrial applications.
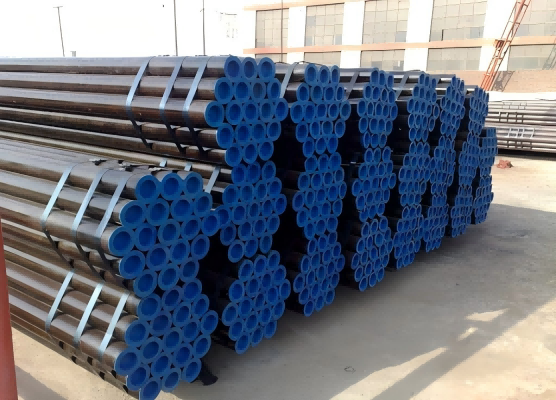

- API 5L Seamless pipeline
API 5L Seamless Pipeline Tube X42-X70 PSL2 Energy Transportation
Email:
sales@imristeel.com
Phone:
+86 13646172523
Quote Now
Product Detail
Chemical Component
Related Products


Quick Details
Product Name:
API 5L Seamless Pipeline Tube X42-X70 PSL2 Energy Transportation
Standard:
API SPEC 5L
Grade:
A B C X42~X70
Thickness:
3.5-60mm
Section Shape:
Round
Outer Diameter:
Ф38-457
Place of Origin:
Baotou, China(Mainland)
Usage:
Gas and Oil Transportation
Surface Treatment:
Hot Rolled
Tolerance:
WT: -12.5% ~ +15% OD: ±0.075D
End:
Plain,beveled,cutting,threading.flange or customized
End Protector:
Plastic pipe caps,iron protector or customized
length:
6-12m
Brand:
Baotou steel
Delivery Time:
Normally within 30-45 days and according to the quantity.
Chemical Component
Chemical Composition for API 5L PSL 2 Pipe with t ≤ 25.0 mm (0.984 in.)
| Steel Grade (Steel Name) | Mass Fraction, Based on Heat and Product Analyses % max | Carbon Equivalent a % max | |||||||||
| C b | Si | Mn b | P | S | V | Nb | Ti | Other | CE IIW | CE pcm | |
| Seamless Pipe | |||||||||||
| L245R or BR | 0.24 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.015 | c | c | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L290R or X42R | 0.24 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L245N or BN | 0.24 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.015 | c | c | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L290N or X42N | 0.24 | 0.40 | 1.20 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L320N or X46N | 0.24 | 0.40 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | d,e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L360N or X52N | 0.24 | 0.45 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.04 | d,e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L390N or X56N | 0.24 | 0.45 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.10 f | 0.05 | 0.04 | d,e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L415N or X60N | 0.24 f | 0.45 f | 1.40 f | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.10 f | 0.05 f | 0.04 f | g,h,l | As agreed | |
| L245Q or BQ | 0.18 | 0.45 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L290Q or X42Q | 0.18 | 0.45 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L320Q or X46Q | 0.18 | 0.45 | 1.40 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L360Q or X52Q | 0.18 | 0.45 | 1.50 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 | e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L390Q or X56Q | 0.18 | 0.45 | 1.50 | 0.025 | 0.015 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.04 | d,e,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L415Q or X60Q | 0.18 f | 0.45 f | 1.70 f | 0.025 | 0.015 | g | g | g | h,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L450Q or X65Q | 0.18 f | 0.45 f | 1.70 f | 0.025 | 0.015 | g | g | g | h,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L485Q or X70Q | 0.18 f | 0.45 f | 1.80 f | 0.025 | 0.015 | g | g | g | h,l | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| L555Q or X80Q | 0.18 f | 0.45 f | 1.90 f | 0.025 | 0.015 | g | g | g | i,j | As agreed | |
| L625Q or X90Q | 0.16 f | 0.45 f | 1.90 | 0.020 | 0.010 | g | g | g | j,k | As agreed | |
| L690Q or X100Q | 0.16 f | 0.45 f | 1.90 | 0.020 | 0.010 | g | g | g | j,k | As agreed | |
| a Based on product analysis, for seamless pipe with t > 20.0 mm (0.787 in.), the CE limits shall be as agreed; the CE IIW limits apply if C > 0.12 % and the CEpcm limits apply if C ≤ 0.12 %. b For each reduction of 0.01 % below the specified maximum for C, an increase of 0.05 % above the specified maximum for Mn is permissible, up to a maximum of 1.65 % for grades ≥ L245 or B, but ≤ L360 or X52; up to a maximum of 1.75 % for grades > L360 or X52, but < L485 or X70; up to a maximum of 2.00 % for grades ≥ L485 or X70, but ≤ L555 or X80; and up to a maximum of 2.20 % for grades > L555 or X80. c Unless otherwise agreed, Nb + V ≤ 0.06 %. d Nb + V + Ti ≤ 0.15 %. e Unless otherwise agreed, Cu ≤ 0.50 %; Ni ≤ 0.30 %; Cr ≤ 0.30 % and Mo ≤ 0.15 %. f Unless otherwise agreed. g Unless otherwise agreed, Nb + V + Ti ≤ 0.15 %. h Unless otherwise agreed, Cu ≤ 0.50 %; Ni ≤ 0.50 %; Cr ≤ 0.50 % and Mo ≤ 0.50 %. i Unless otherwise agreed, Cu ≤ 0.50 %; Ni ≤ 1.00 %; Cr ≤ 0.50 % and Mo ≤ 0.50 %. j B ≤ 0.004 %. k Unless otherwise agreed, Cu ≤ 0.50 %; Ni ≤ 1.00 %; Cr ≤ 0.55 % and Mo ≤ 0.80 %. i For PSL 2 pipe grades except those grades to which footnote j) already applies, the following applies: unless otherwise agreed no intentional addition of B is permitted and residual B ≤ 0.001 % | |||||||||||
Mechanical Performance
Requirements for the Results of Tensile Tests for API 5L PSL 2 Pipe
| Pipe Grade | Pipe Body of Seamless Pipe | Weld Seam of HFW, SAW and COW Pipe | |||||
| Yield Strength a Rt0.5 MPa (psi) | Tensile Strength a Rm MPa (psi) | Ratio a,c Rt0.5/Rm | Elongation (on 50 mm or 2 in.) Af % | Tensile Strength d Rm MPa (psi) | |||
| min | max | min | max | max | min | min | |
| L245R or BR L245N or BN L245Q or BQ L245M or BM | 245 (35,500) | 450 (65,300) e | 415 (60,200) | 655 (95,000) | 0.93 | f | 415 (60,200) |
| L290R or X42R L290N or X42N L290Q or X42Q L290M or X42M | 290 (42,100) | 495 (71,800) | 415 (60,200) | 655 (95,000) | 0.93 | f | 415 (60,200) |
| L320N or X46N L320Q or X46Q L320M or X46M | 320 (46,400) | 525 (76,100) | 435 (63,100) | 655 (95,000) | 0.93 | f | 435 (63,100) |
| L360N or X52N L360Q or X52Q L360M or X52M | 360 (52,200) | 530 (76,900) | 460 (66,700) | 760 (110,200) | 0.93 | f | 460 (66,700) |
| L390N or X56N L390Q or X56Q L390M or X56M | 390 (56,600) | 545 (79,000) | 490 (71,100) | 760 (110,200) | 0.93 | f | 490 (71,100) |
| L415N or X60N L415Q or X60Q L415M or X60M | 415 (60,200) | 565 (81,900) | 520 (75,400) | 760 (110,200) | 0.93 | f | 520 (75,400) |
| L450Q or X65Q L450M or X65M | 450 (65,300) | 600 (87,000) | 535 (77,600) | 760 (110,200) | 0.93 | f | 535 (77,600) |
| L485Q or X70Q L485M or X70M | 485 (70,300) | 635 (92,100) | 570 (82,700) | 760 (110,200) | 0.93 | f | 570 (82,700) |
| L555Q or X80Q L555M or X80M | 555 (80,500) | 705 (102,300) | 625 (90,600) | 825 (119,700) | 0.93 | f | 625 (90,600) |
| L625M or X90M | 625 (90,600) | 775 (112,400) | 695 (100,800) | 915 (132,700) | 0.95 | f | 695 (100,800) |
| L625Q or X90Q | 625 (90,600) | 775 (112,400) | 695 (100,800) | 915 (132,700) | 0.97 g | f | |
| L690M or X100M | 690 (100,100) b | 840 (121,800) b | 760 (110,200) | 990 (143,600) | 0.97 h | f | 760 (110,200) |
| L690Q or X100Q | 690 (100,100) b | 840 (121,800) b | 760 (110,200) | 990 (143,600) | 0.97 h | f | |
| L830M or X120M | 830 (120,400) b | 1050 (152,300) b | 915 (132,700) | 1145 (166,100) | 0.99 h | f | 915 (132,700) |
| a For intermediate grades, the difference between the specified maximum yield strength and the specified minimum yield strength shall be as given in the table for the next higher grade, and the difference between the specified minimum tensile strength and the specified minimum yield strength shall be as given in the table for the next higher grade; for intermediate grades up to Grade L320 or X46, the tensile strength shall be ≤ 655 MPa (95,000 psi); for intermediate grades greater than Grade L320 or X46 and lower than Grade L555 or X80, the tensile strength shall be ≤ 760 MPa (110,200 psi); for intermediate grades higher than Grade L555 or X80, the maximum permissible tensile strength shall be obtained by interpolation; for SI units, the calculated value shall be rounded to the nearest 5 MPa; for USC units, the calculated value shall be rounded to the nearest 100 psi. b For grades > L625 or X90, Rp0.2 applies. c This limit applies for pipe with D > 323.9 mm (12.750 in.). d For intermediate grades, the specified minimum tensile strength for the weld seam shall be the same value as was determined for the pipe body using footnote a). e For pipe requiring longitudinal testing, the maximum yield strength shall be ≤ 495 MPa (71,800 psi). f The specified minimum elongation, Af, shall be as determined using the following equation: Af = C where C is 1940 for calculations using SI units and 625,000 for calculations using USC units; Axc is the applicable tensile test piece cross-sectional area, expressed in square millimeters (square inches), as follows: 1) for circular cross-section test pieces, 130 mm2 (0.20 in.2) for 12.7 mm (0.500 in.) and 8.9 mm (0.350 in.) diameter test pieces; 65 mm2 (0.10 in.2) for 6.4 mm (0.250 in.) diameter test pieces; 2) for full-section test pieces, the lesser of a) 485 mm2 (0.75 in.2) and b) the cross-sectional area of the test piece, derived using the specified outside diameter and the specified wall thickness of the pipe, rounded to the nearest 10 mm2 (0.01 in.2); 3) for strip test pieces, the lesser of a) 485 mm2 (0.75 in.2) and b) the cross-sectional area of the test piece, derived using the specified width of the test piece and the specified wall thickness of the pipe, rounded to the nearest 10 mm2 (0.01 in.2); U is the specified minimum tensile strength, expressed in megapascals (pounds per square inch). g Lower values of Rt0.5/Rm may be specified by agreement. h For grades > L625 or X90, Rp0.2 /Rm applies. Lower values of Rp0.2 /Rm may be specified by agreement. | |||||||
Pipeline Tubes: Key Applications Across Industries
Pipeline tubes are critical components in numerous industries, ensuring efficient and safe transportation of fluids, gases, and other materials. Below are the major application fields where pipeline tubes play a vital role:
- Oil & Gas Industry
– Oil pipelines: Transport crude oil from extraction sites to refineries.
– Natural gas pipelines: Distribute gas for residential, commercial, and industrial use.
– Offshore pipelines: Subsea applications for deepwater oil and gas exploration.
- Water & Wastewater Management
– Water supply pipelines: Deliver potable water to urban and rural areas.
– Sewage pipelines: Transport wastewater to treatment plants.
– Irrigation pipelines: Support agricultural water distribution.
- Chemical & Petrochemical Industry
– Chemical pipelines: Transfer corrosive and hazardous fluids safely.
– Petrochemical pipelines: Transport refined products like ethylene and propylene.
- Power Generation & Energy Sector
– Steam pipelines: Used in thermal power plants.
– Hydropower pipelines: Channel water to turbines for energy production.
- Mining & Slurry Transport
– Slurry pipelines: Move ore, tailings, and mineral concentrates efficiently.
- Infrastructure & Urban Development
– District heating/cooling pipelines: Enable energy-efficient HVAC systems.
– Municipal pipelines: Support urban utility networks.
- Industrial Manufacturing
– Compressed air pipelines: Supply factories with pneumatic power.
– Process pipelines: Facilitate material handling in production lines.
Related products


API 5CT J55 Oil Casing Pipe Size 4.5"to 20"
Read More 




Corrosion Resistant API 5CT L80-1 Tubing
Read More 




Heavy Rail of P50/R50 Rails
Read More 




APL 5L X65 Oil and Gas Pipeline
Read More 




OCTG API 5CT J55 Oil Well Tubing
Read More 




API 5L Seamless Pipeline X42-X70 PSL1 Oil and Gas Industry
Read More 




APL 5L X52 Oil and Gas Pipeline
Read More 




3PP Anti-Corrosion Coated Pipe
Read More 







